Most promissory notes have an explicit interest charge, and although some notes are labeled as “zero interest,” there is often a fee built into the note.
Hello and welcome to Viewpoint
CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path. In January, the clock starts ticking on the 16th, which means there is no interest accruing during the first 15 days, just the last 16. Interest accrues all through February, and the note is then due on the 75th day.
Financial Accounting
There are three simple steps to determining the interest liability on a loan note, so you’ll know the total amount you’re paying. Click here to extend your session to continue reading our licensed content, if not, you will be automatically logged off. Once you have viewed this piece of content, to ensure you can access the content most relevant to you, please confirm your territory. These materials were downloaded from PwC’s Viewpoint (viewpoint.pwc.com) under license.
- A leveraged buyout (LBO) is a transaction in which a company or business is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to meet the cost of acquisition.
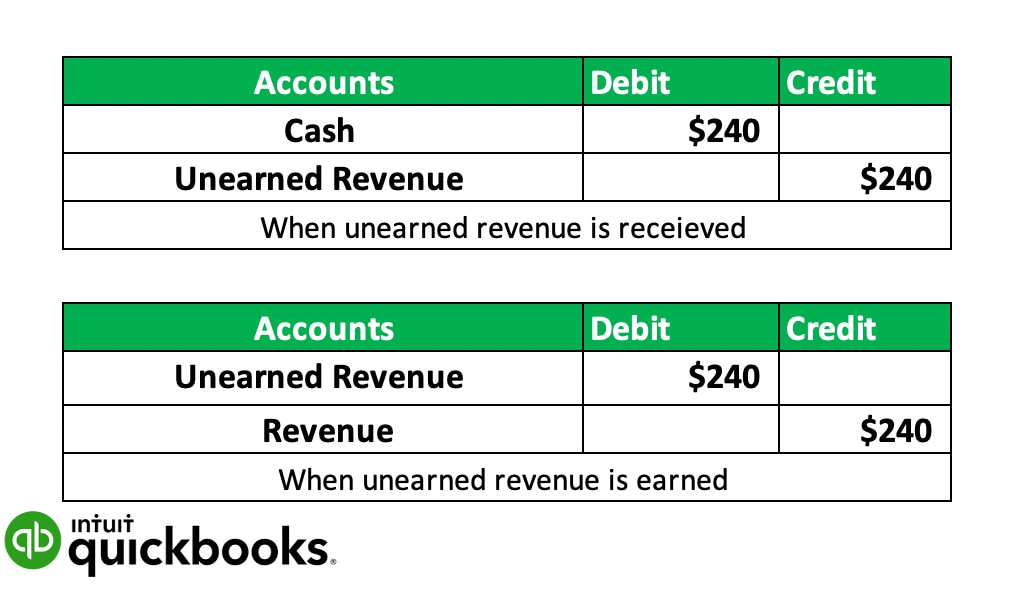
- Using this formula, we can calculate interest revenue in the previous example.
- Interest revenue is the interest that an entity earns from the money it has lent or the investments it has made.
- Therefore, a bank would record interest revenue in the revenue section at the top of the income statement.
IAS 18 Revenue
Learn to calculate it accurately using specific formulas and then apply this knowledge in practical, real-world business scenarios. The article also highlights common misinterpretations and mistakes to avoid while examining and managing interest revenue in business scenarios. Interest income is usually taxable income and is presented in the income statement for the simple reason that it is an income account. Usually, the two categories in the income statement, namely “Income from Operations” and “Other Income” are listed separately. In such an instance, the presentation of interest income will largely depend on the nature of the business’ primary operations.
As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. IFRS Accounting Standards are, in effect, a global accounting language—companies in more than 140 jurisdictions are required to use them when reporting on their financial health. The IASB is supported by technical staff and a range of advisory bodies. On the other hand, interest revenue may not be the primary source of income for different companies, such as automobile companies or electronics companies. In such cases, the interest income is generated for these companies from ancillary activities. These companies record interest income in the ‘Other Revenue and Expense’ section of the income statement.
1 Chapter overview — interest income
It affects the income statement where it increases total revenue and net income, and it also impacts the balance sheet, contributing to the increase in total assets. At the end of every month, the account statement will reflect the interest that the bank pays for borrowing the account holder’s money. It is important to note that banks use what is called “fractional banking,” which means that only a part of customer deposit accounts can be used by the bank as lending funds. The bank must retain a certain level – known as the reserve – of deposit account funds. It cannot legally loan out all the funds that customers have deposited with it. A very simple example of interest income that happens every day is when an individual deposits money into a savings account and decides to leave it untouched for several months or years.
Businesses record their financial transactions in the books of accounts on the basis o the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). A company following GAAP would record both interest revenue and interest receivables in the designated sections of the income statement. A company will either follow an accrual accumulated depreciation definition basis of accounting or a cash basis of accounting. This journal entry is made to eliminate the receivable that the company has recorded at the adjusting entry of the previous period. At the same time, it is to record the interest income that the company has earned during the current accounting period.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs. Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates. CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
Interest revenue is calculated and recorded separately of interest receivable. A note generally creates interest income even though the interest has yet to be paid in cash by the borrower. It’s also worth noting that this revenue stream has a significant impact on the company’s financial statements.
Interest revenue is classified as an income stream or part of a company’s operating income on the income statement. Interest Revenue can be defined as the earnings generated by a company from its lending or investing activities. That revenue represents interest earned in October, November, and December. The remainder will be recognized in January when the entire amount is paid. Discover the key financial, operational, and strategic traits that make a company an ideal Leveraged Buyout (LBO) candidate in this comprehensive guide. Everything you need to know to calculate an interest rate with the present value formula.
If an entity disposes of property, plant and equipment at the end of its useful economic life the proceeds of disposal are not revenue for the entity. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the Interest Revenues account reports the interest earned by a company during the time period indicated in the heading of the income statement. Interest Revenues account includes interest earned whether or not the interest was received or billed. Interest Revenues are nonoperating revenues or income for companies not in the business of lending money. For companies in the business of lending money, Interest Revenues are reported in the operating section of the multiple-step income statement.